IoT Device Management: Ensuring Efficiency, Security, and Scalability
The Internet of Things is transforming industries, homes, and how things are done. With a growing number of devices connected, managing these becomes critical. IoT device management oversees the lifecycle of the connected devices, makes their security a priority, and enhances their performance.
What is IoT Device Management?
IoT device management is the secure registrar, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance process for all devices throughout their lifespan. It ensures that connected devices have perfect performance, security, and updatability.
Essential Key Components of IoT Device Management:
1.Device Registration and Authentication
Gaining assurance that only authorized devices are listed in the network.
2. Configuration and Control
Access to reconfigure and update the devices remotely.
3. Monitoring and Diagnostics
Consistent monitoring and tracing of the performance of the devices and various problems arising from their usage.
4. Security Management
It protects devices and data from cyber threats.
How does IoT device management work?

IoT device management makes it possible to control the complete life cycle of IoT devices, from the initial provisioning to retirement, and everything in between.
1. Device onboarding
Device onboarding is the first step of IoT device management. Onboarding is referred to as the very initial device configuration which involves changing the original settings applied to the off-the-shelf device into settings which will help the device to be integrated with your network.
After provisioning, it also requires authentication by verifying the device’s identity when added into the IoT system and authenticating users at login. It ensures that the enrolled devices are authorized and no unauthorized access takes place, thus completely keeping the proprietary information safe from intrusions.
IoT device management platforms that support bulk device registration make onboarding simpler and faster by enabling you to onboard hundreds and thousands of devices at a time.
2. Device view
Get complete visibility over all your IoT devices in one place. A device list helps you sort through devices by searching and filtering devices so you can find exactly what you need when you need it.
3. Device configuration
Devices and networks are not fixed objects. Instead, they constantly change. IoT device management can be done during more stages than just the provisioning stage. One of the configurations includes factors like firmware, networking, access permissions, or other properties.
4. Device grouping
Efficient IoT device management requires scaling from a small set of devices to thousands or more and then keeping each one updated with firmware and other configuration updates. Organize your devices by grouping them by functionality, location, or other characteristics into top-level groups, subgroups, or dynamically constructed smart groups. Grouped devices enable easier management of devices and support for bulk operations.
5. Diagnostics
Perform diagnostics for every IoT appliance, from the individual unit to the whole network of devices. Troubleshoot and correct problems quickly without causing system downtime.
6. Status Monitoring
Understand the functioning of individual devices or a cluster of your choice. Understand user-defined data points such as temperature or vibration. Establish for user-defined notifications to cause decisions, such as events associated with a requirement for preventive maintenance to extend equipment life. Identify and rectify conditions that would cause unauthorized access, for example, device configuration change attempts. Monitor device alarms to ensure in-spec operations.
7. Device security
IoT security is a definite do-or-die to conduct business in this connected world. There is the option of firmware updates from IoT device management that helps ensure that devices are on the latest secure software. Architect the architecture of the IoT device management platform to be built to protect physical, network, application and access control.
entire installation of deployed devices, and routing data from devices to the right users and dashboards possible.
Empowering Muscat with Next-Gen IoT Automation
Muscat Automation is changing industries by offering advanced IoT automation services, enabling companies to maximize processes, reduce costs, and achieve unmatched efficiency through IoT automation, which connects devices and systems to allow for seamless communication, real-time data monitoring, and intelligent decision-making.
Muscat Automation focuses on innovating through cutting-edge IoT solutions customized for various sectors like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and smart homes. From predictive maintenance in factories to smart energy management systems in homes, their solutions serve both operational and sustainability purposes.
By embracing IoT automation, businesses in Muscat can utilize the power of insights in real-time, simplify repetitive works, and increase productivity in general. Staying ahead, Muscat Automation remains at the forefront in the integration of technology and industry needs.
Empowering Muscat for a Smarter Tomorrow.
Transform your business today with Next-Gen IoT Automation by Muscat Automation.
IoT Device Monitoring: Ensuring Operational Continuity
What is IoT Device Monitoring?
IoT device monitoring is continuously tracking and analyzing IoT devices’ performance, health, and security. It helps maintain device functionality, ensures uptime, and optimizes operational efficiency.
Some essential tasks are as follows:
Tracking of connectivity status
Monitoring of data flow between devices
Identifying strange behaviour or errors
Improved system reliability.
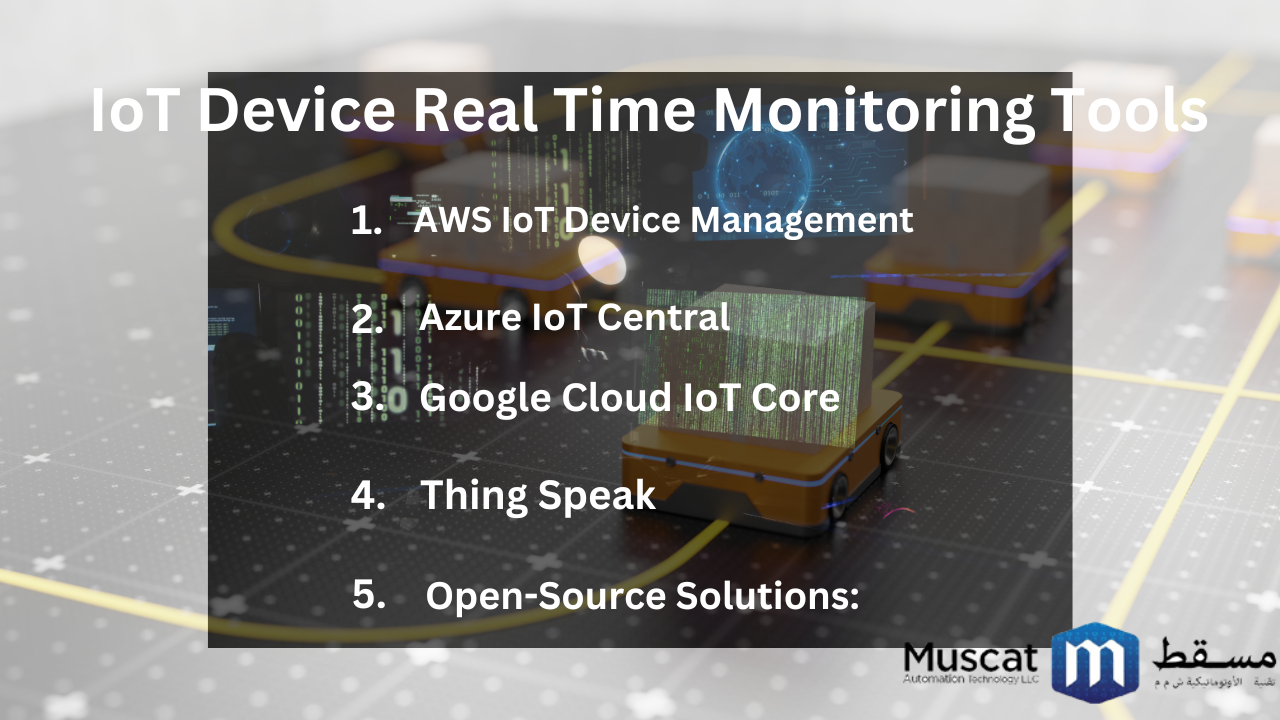
Real-Time Monitoring Tools
1. AWS IoT Device Management:
allows monitoring, updating, and securing devices.
2. Azure IoT Central:
scalable, real-time monitoring and diagnostics solution.
3. Google Cloud IoT Core:
integrates and monitors with devices through real-time analytics.
4. Thing Speak:
This is a popular IoT data gathering, visualization, and analysis application.
5. Open-Source Solutions:
Zabbix and Prometheus are widely used IoT monitoring tools in cost-sensitive environments.
Although these tools provide adequate information on the device’s performance, they can also automate routine tasks such as firmware updates and issue resolution
Benefits of IoT Device Monitoring

Preemptive Detection of Issues
The monitoring system provides potential issues before they get serious. Therefore, this minimizes downtimes and costly overhauls.

Proactive Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Real-time alerts and diagnostics help teams troubleshoot issues immediately, thus reducing manual interference and ensuring seamless execution.

Data-Driven Decision Making
Insights obtained from monitored devices assist companies in making decisions, optimizing processes, and predicting future demands.

Security
Such monitoring tools track unusual behavior of devices and add extra layers of protection against cyber threats.

Improved Customer Experience
Reliability for consumer-facing IoT results from proactive monitoring, leading to better customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for IoT Device Management
1. Develop a Strong Strategy
Develop a strategic plan encompassing device lifecycle management, security procedures, and monitoring processes. Be clear on goals and resource allocation.
2. Scalability
Design the systems to manage large numbers of devices, increased data, and more in ways that do not impact their performance.
3. User Training and Support
Prepare your team to effectively handle the systems and provide constant support in case of challenges towards continuity of operations.
4. Integrating Muscat Automation
They leverage Muscat automation tools for device configuration, firmware updates, and issue resolution to reduce manual effort and efficiency.
Streamline operations-through Muscut automation tools, devices are easily onboarded, configured, and updated.
5. Monitor Efficiency
Use real-time analytics to track device performance and health with minimal human intervention.
6. Error Reduction
Use automation to minimize errors in repetitive tasks, ensuring higher accuracy and reliability.